technology
TagHIPAA Security Rule Changes 2025: What Your Healthcare Practice Must Know Now
Healthcare data breaches have exploded over the last five years. The number of affected people rose by a staggering 1002% between 2018 and 2023. More than 167 million people faced the consequences in 2023 alone. This crisis has pushed the HIPAA Se…
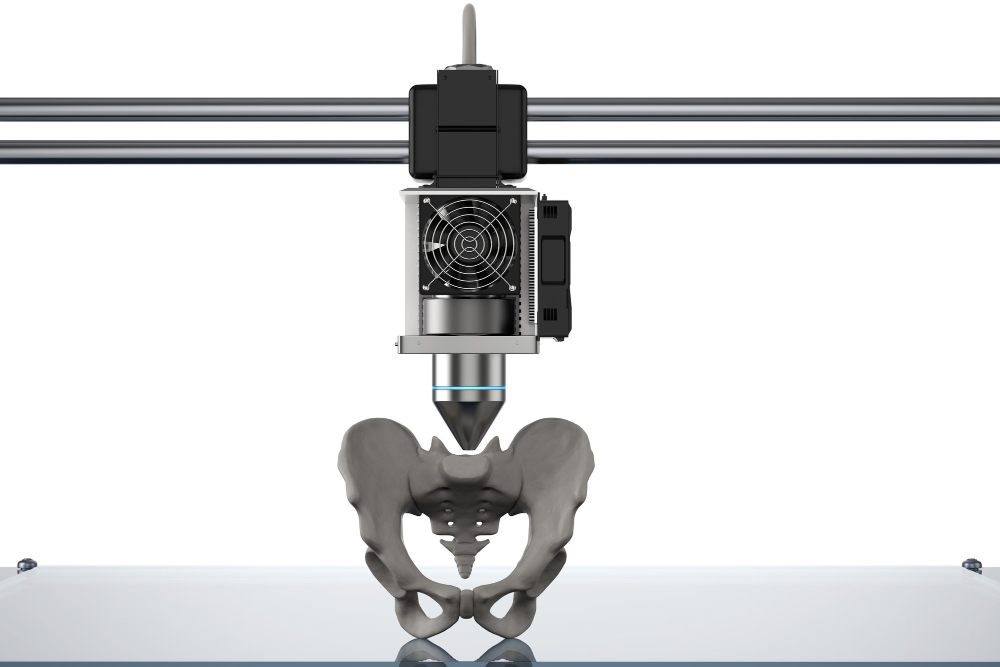
Medical 3D Printing Explained: From CT Scan to Custom Implants
Medical 3D printing has changed from a niche technology into a healthcare revolution. The global market is expected to reach $6.08 billion by 2027. Only three hospitals had in-house 3D printing facilities in 2010. This number jumped to 113 facilit…
Navigating the New Era of Patient-Centered Care in 2025
The year 2025 will mark a transformative period in healthcare as patient-centered care becomes increasingly prominent. This paradigm shift emphasizes treating patients as individuals with unique needs and preferences, fundamentally reshaping the p…
How Streamlining Hospital Processes Can Lead to Improved Patient Outcomes
We’ve all worked our way through the slow-moving bowels of the American healthcare system at one point or another. Maybe you had to fight your way to an appointment with a specialist who is apparently booked out six months in advance. Maybe you ne…
How AI and Technology Are Transforming Nursing Practice
In 2024, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and advanced technologies into healthcare is not just a futuristic concept—it’s our present reality. Nurses, as frontline caregivers, are at the forefront of this technological revolution. L…
How AI is Revolutionizing Treatment and Wellness
The Future of Healthcare
The health care industry is making some transformations, to turn over the industry in the hands of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The technology’s adoption in the health sector will focus on personalized care, with supervi…
Cybersecurity in Healthcare: Protecting Patient Data in an Increasingly Digital World
Healthcare’s reliance on digital technology for patient management and data storage has made cybersecurity a top priority. Protecting sensitive patient information from cyber threats is essential to maintain trust, comply with regulations, and ens…
Extended Reality in Healthcare: Applications in Training, Treatment, and Patient Education
XR is a powerful tool that enhances learning for a broad spectrum of healthcare professionals, from surgeons to nurses:
- Surgical Simulations: VR-based surgical simulations provide hands-on practice in a safe, controlled setting, allowing surg…
The Rise of Digital Therapeutics: Software as a Medical Treatment
Digital therapeutics (DTx) represent a new frontier in healthcare, offering evidence-based therapeutic interventions driven by high-quality software programs to prevent, manage, or treat a medical disorder or disease. This innovative approach is r…
The Impact of Social Media on Healthcare: Navigating Misinformation and Leveraging Opportunities
Social media has become an integral part of modern life, significantly influencing how people access, share, and interpret health information. For healthcare providers, understanding the impact of social media on healthcare is crucial for addressi…