healthcare
TagStress Relief Tips for Healthcare Workers
Up to 70% of healthcare workers feel stressed according to a newly released 2023 study. While having high amounts of stress isn’t good for anyone, it can result in unique consequences for healthcare workers, says Dr. Jenna Sage. This makes it espe…
Job Opportunities in Nursing: A Sector-by-Sector Breakdown
Do you find fulfillment in helping others and making a tangible impact on people’s lives? If so, a career in nursing might be the ideal path for you. Nursing is not just a profession but a calling that offers diverse opportunities. With an aging p…
Five Technological Skills for Accelerating Your Healthcare Career
During the height of the pandemic hospitals were faced with an unprecedented demand for their services. At the same time, they were also forced to make do with fewer personnel than they were accustomed to as nurses and doctors resigned from their …
Exploring the Importance of Communication Skills in the Healthcare Industry
The world relies so much on the healthcare industry. It employs thousands of new workers every year. It’s where people go to get care and improve their holistic health. And we rely on healthcare professionals of various disciplines to develop new …
Contemplating a Career Move in the Nursing Industry – Exploring New Horizons of Healing and Growth
Almost half of all nurses leave the profession entirely after just five years on the job. The reason is pretty simple. Nursing is hard. The hours are brutal. The labor is both physically intensive and mentally exhausting. The pay, though higher th…
Tech Investments That Are Worth It for Medical Practices
There are tech solutions out there for all kinds of business needs these days, from social media management to payroll. As a small business owner keeping an eye on expenses, knowing which tools are worth investing in isn’t always easy. The questio…
The Best Podcasts for Nurses: Empowering, Informative, and Inspiring
Podcasts have exploded in popularity for a reason. They are entertaining, informative, and a great way to pass the time. Since podcasts can be streamed or downloaded, you can listen to them nearly anywhere. With the option to choose from short epi…
How Does Holistic Care Fit in with Existing Models?
Health is a complex state involving a huge number of different systems within the body. These systems are all deeply interconnected, making it difficult to treat one aspect of health without treating the person as a whole. That’s the goal for devo…
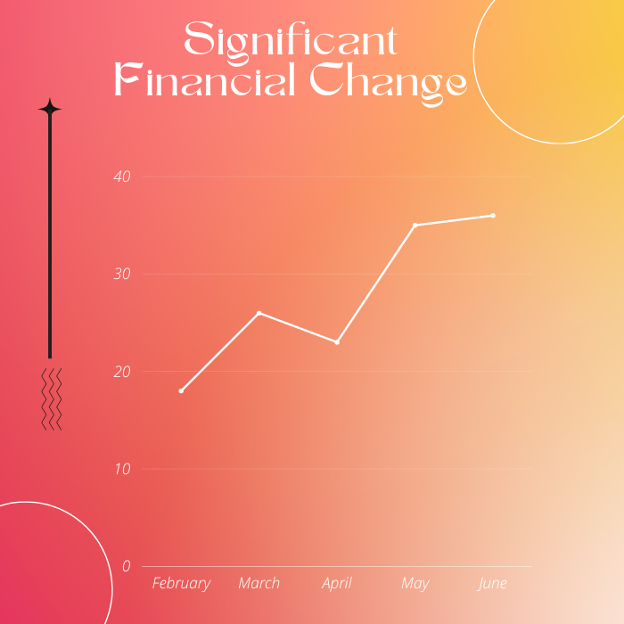
Turn Your Healthcare RCM Metrics into Action & Drive Significant Financial Change
Delivering standard medical aid to the patients while maintaining profitability is the primary objective of every health care provider. Achieving this balance is no doubt the key to a successful health care business. Moreover, physicians seem more…
Using Medical Technology To Make a Difference in Patient Health Outcomes
Medical professionals are often highly significant individuals whose careers greatly influence their patients’ quality of life.Their combination of education, experience, and skills also makes these workers invaluable contributors to public healt…